HOLD MY HEART IN YOUR HAND / 환자의 심장 손에 들고 보듯
HOLD MY HEART IN YOUR HAND / 환자의 심장 손에 들고 보듯
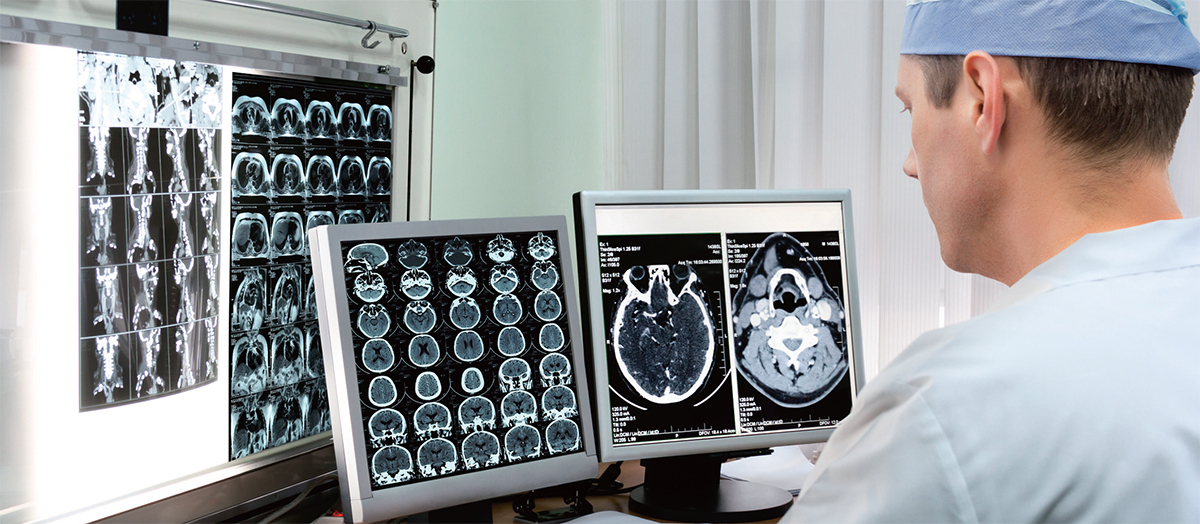
HOLD MY HEART IN YOUR HAND
“Doctors are trying to extract 3-D information from flat slices,” says Sergio Aguirre, the founder and chief technology officer of EchoPixel, a tech company trying to solve the flat-screen problem. “We found they are looking at flat image slices, and correlating between images, and in the process, forgetting what they are looking at.” He says that in their research, they found that doctors are trained to move from one 2-D image to the next, memorizing the orientation of each image as they go. But, he says, “they may forget a key feature that will lead them to lose important diagnostic information. It is a small mental lapse that’s happening from data overload.”
EchoPixel has designed medical visualization software that takes those 2-D slices, reconfigures the anatomy into its proper 3-D spatial structure and beams a depiction of the tissue and organs as if they were real physical objects hovering over a display board. The idea is to enable doctors (wearing 3-D glasses)to lift a skull off the screen with a hand-directed stylus, zoom in on aneurysms and freely rotate the hovering image so they can look at it from many angles. The software has potential in medical school, patient communication and, most important, diagnostic accuracy.
In training trials, radiologists using the software were able to cut their diagnosis time in visual colonoscopies from 30 minutes down to five to 10 minutes, and increased the detection rate of flat lesions—difficult-to-detect and often-overlooked precancerous tissue—by 20 percent. In another trial, Stanford University radiologists were able to use the 3-D images to generate improved surgical plans for major aortopulmonary collateral arteries, a heart condition, decreasing surgery time from four hours to 1.5 hours.
The 3-D platform was recently approved by the FDA for clinical use, and units have already been installed at Stanford University, the University of California, San Francisco; Foxconn Technology Group; and Cleveland Clinic. The company says that the cost of the technology is comparable to—and in many cases, even cheaper than—the 2-D workstations currently considered the standard in health care facilities.
“There’s no reason that, within a few years, anyone should be looking at a 2-D model,” says Aguirre. EchoPixel is also about to begin a colonoscopy trial with real patients, and are working on a data-sharing system aimed at helping doctors across disciplines work together seamlessly on the same 3-D image sets. Universal adoption could have an untold impact on health care.
“All you have to do is look at how CT and MRI affected health care,” says Dr. David Langer, chief of neurosurgery at Lenox Hill Hospital. “All of a sudden we saw things we never saw before, and we started to develop new strategies for treating problems we never knew about. [3-D imaging] could result in absolutely the same thing.”
환자의 심장 손에 들고 보듯
“의사들은 단편적인 평면 이미지에서 3차원 정보를 추출하려 애쓴다”고 에코픽셀의 세르지오 아기레 최고기술책임자(CTO)가 말했다. 그는 이 같은 평면적 이미지 문제를 해결해보려 회사를 창업했다. “지켜봤더니 의사들이 단편적인 평면 이미지를 보면서 상관관계를 추정하는데 그 과정에서 자신들이 본 것을 망각하는 문제가 있었다.” 조사 결과 의사들은 하나의 2차원 이미지에서 다음 이미지로 넘어가면서 각 이미지의 배치를 기억하도록 교육받았다고 한다. 그러나 “의사들이 주요 특징을 망각해 중요한 진단 정보를 놓치게 될 가능성도 있다. 이는 데이터 과잉에서 비롯되는 두뇌의 작은 오류다.”
에코픽셀이 개발한 의료 가시화 소프트웨어는 이들 단편적인 2차원 이미지들을 토대로 인체를 적당한 3D 공간 구조로 재구성한다. 그리고 조직과 장기 이미지를 쏘아 보내 마치 스크린 상에 실제 장기가 떠 있는 듯 보이게 한다. 의사들이 3D 안경을 착용한 채 손짓으로 철필을 움직여 스크린 상의 두개골을 열고 뇌동맥류를 확대시킨다. 그리고 이미지를 원하는 대로 회전시켜 여러 각도에서 볼 수 있도록 한다는 구상이다. 이 소프트웨어는 메디컬 스쿨, 환자 커뮤니케이션, 그리고 무엇보다도 진단의 정확성 제고에 유용할 것으로 예상된다.
트레이닝 실험에서 가시화 소프트웨어를 이용한 방사선과 의사들은 대장내시경 검사 진단시간을 30분에서 5~10분으로 단축할 수 있었다. 그리고 평탄 병변의 검출률을 20% 높였다. 평탄 병변은 감지하기 어렵고 종종 간과하기 쉬운 전암 조직이다. 또 다른 실험에선 스탠퍼드대학 방사선과 의료진이 이 3D 이미지를 이용해 심장이상인 ‘주요 대동맥-폐동맥 측부혈관’ 수술계획을 개선할 수 있었다. 그 결과 수술 시간이 5시간에서 1.5시간으로 단축됐다.
이 3D 플랫폼은 최근 미국 식품의약국(FDA)으로부터 임상에 이용해도 좋다는 승인을 받았다. 그리고 스탠퍼드대학과 캘리포니아대학(샌프란시스코), 폭스콘 테크놀로지 그룹, 클리블랜드 클리닉은 이미 도입했다. 가격은 현재 건강의료 시설에서 표준으로 삼는 2D 워크스테이션과 비슷하다고(많은 경우 더 싸다고) 에코픽셀은 말한다.
아기레 CTO는 “앞으로 몇 년 이내에 2D 모델을 들여다볼 필요가 없어진다”고 말했다. 에코픽셀은 또한 실제 환자를 대상으로 대장내시경 실험을 시작하려는 참이다. 그리고 하나의 3D 이미지 집합을 토대로 여러 분야의 의사들이 원활한 공조를 이루도록 하는 데이터 공유 시스템을 연구 중이다. 이 기술이 보편화하면 의료계에 엄청난 영향을 미칠 수 있다.
“CT와 MRI가 의학계에 얼마나 큰 영향을 미쳤는지만 봐도 알 수 있다”고 레녹스힐 병원의 데이비드 랭거 신경외과장이 말했다. “갑자기 지금껏 보이지 않던 것들이 보였다. 우리가 전혀 몰랐던 문제를 치료하기 위한 전략을 새로 개발하기 시작했다. 3D 영상기술도 완전히 똑같은 결과를 가져올 수 있다.”
- 번역 차진우
ⓒ이코노미스트(https://economist.co.kr) '내일을 위한 경제뉴스 이코노미스트' 무단 전재 및 재배포 금지
많이 본 뉴스
1SKT, 국내 통신사 최초로 국제표준 'AI 경영시스템' 인증 획득
2 KB국민은행 “홍콩 H지수 상승세…추가 손실 가능성 없어”
3‘블랑’ 맥주, 프랑스서 부동액 검출돼 리콜…“국내용 제품 영향 없다”
4NH투자증권, 1분기 영업익 2769억원…전년比 10.1%↑
5“SU7, 모델 3 이겼다”...테슬라 넘었다는 샤오미
6KB금융, 1분기 순익 1조491…전년比 30.5% ‘털썩’
7베일 벗은 공매도 전산시스템…완비 때까지 ‘공매도 금지’ 연장되나
8KB부동산 “전세안전진단 서비스…10건 중 2건 ‘위험’ 등급”
9파랗게 물든 제네시스, 베이징 모터쇼 사로잡았다






