- 체외에서 혈소판 만든다
LOSS BLEEDER
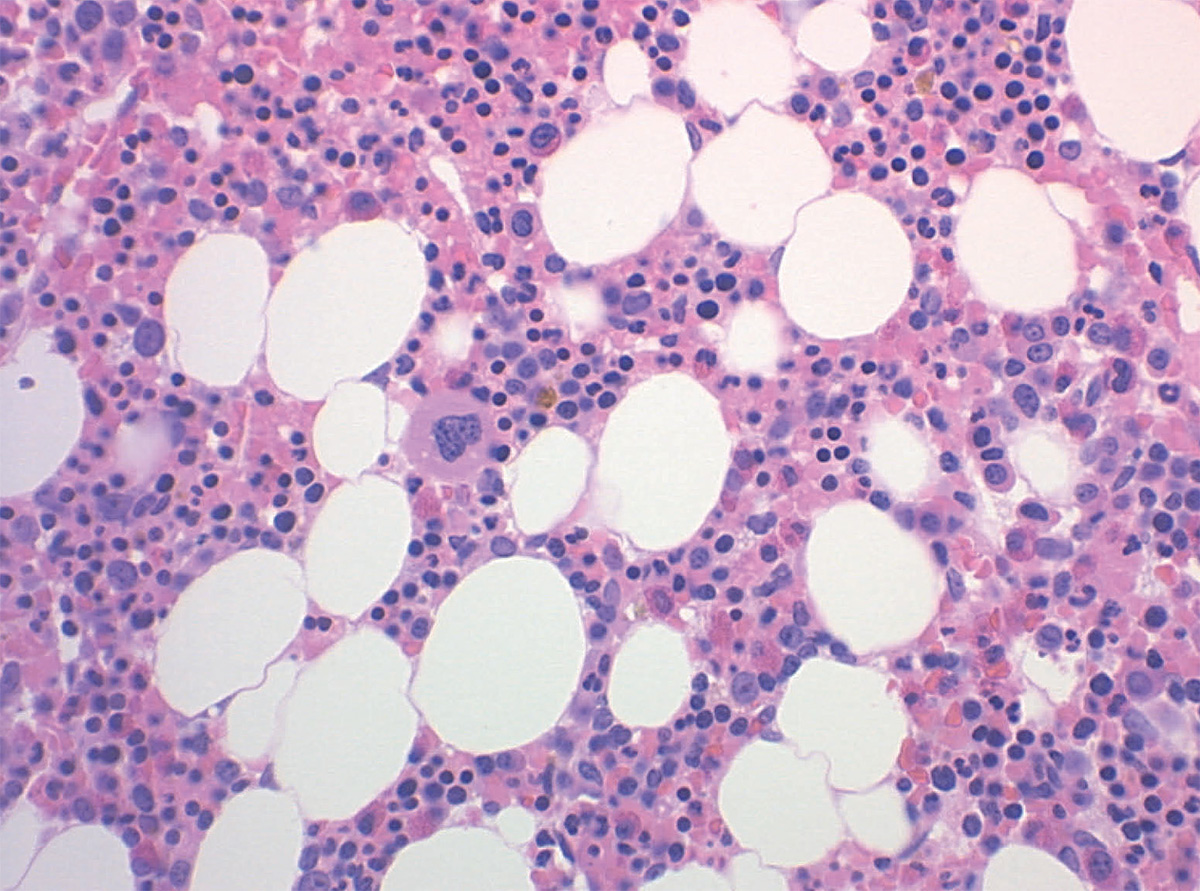
Your blood isn’t the uniform river of red it appears to be. It’s actually made up of many, varied cells. One class of blood cells is the platelets, which are small, and circulate throughout the blood to activate clotting and stop bleeding. When platelet function is impaired—such as in the case of thrombocytopenia, hemophilia and over 200 other conditions, according to the Platelet Disorder Support Association—patients run the risk of bleeding in greater, life-threatening amounts. If the blood does not clot, patients may bleed out and die.
Treatments for platelet function disorders have many drawbacks. Platelet transfusions are common, but the process requires donors, and complications due to immune responses are frequent and unpredictable. Sometimes drugs will be prescribed to block antibodies—immune cells—from attacking platelets. A last resort is the removal of a patient’s spleen, which eliminates a substantial site of antibody production. But even that doesn’t always improve platelet count.
A team of researchers at Tufts University School of Engineering in Massachusetts and the University of Pavia in Italy, however, believe they may have a solution: create functioning human platelets outside of the patient’s body. They’ve created a model that acts exactly like human bone marrow, the environment within the body that stimulates platelet growth.
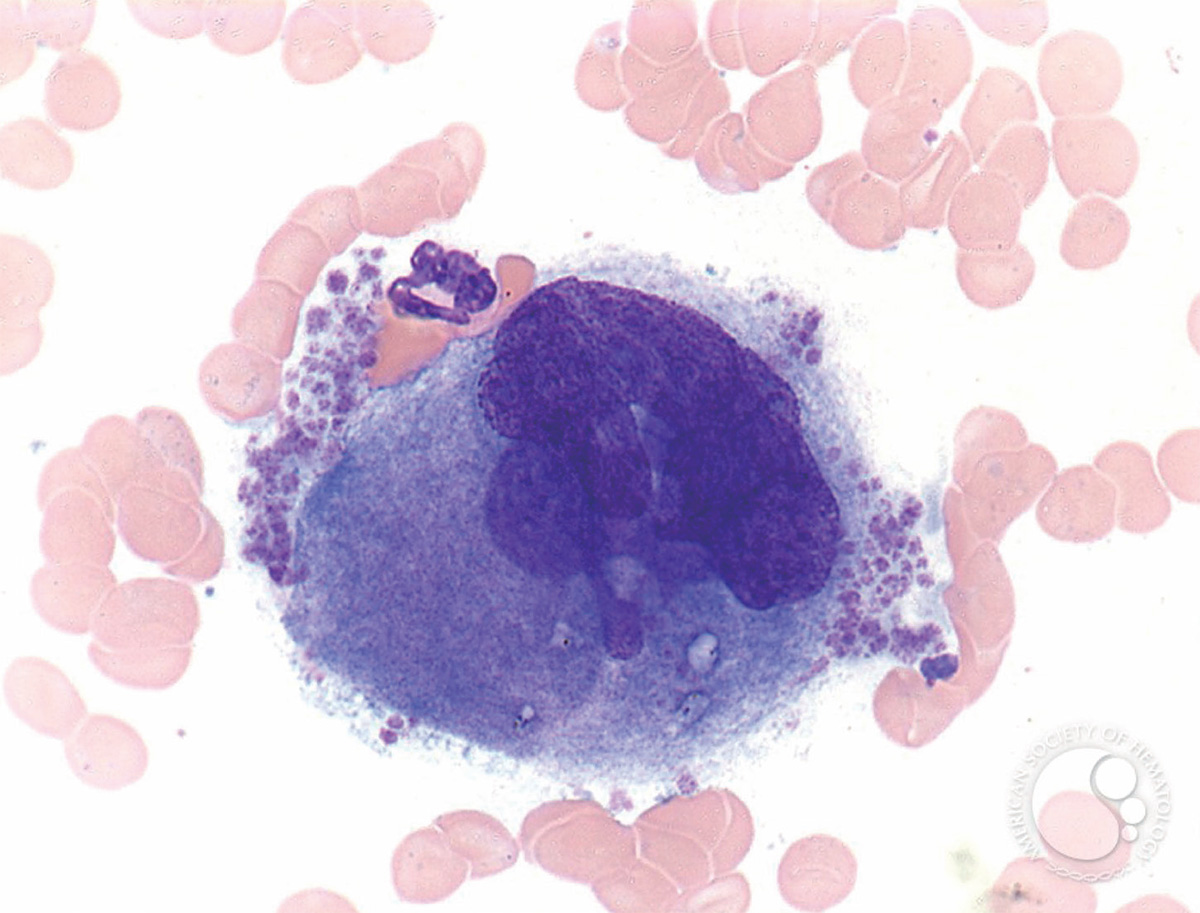
According to Dr. David Kaplan, one of the lead researchers on the team, silk was key to the process. Because of its structure, silk can be made in varying degrees of stiffness and different forms, which researchers have found affects the formation and release of authentic platelets. Most important, silk does not cause the platelets to clot, meaning that functional platelets can be gathered from the system and used later on without the quality and storage problems created by donor platelets.
The system doesn’t yield as many platelets as healthy human bone marrow, but the researchers are optimistic that they can up that. Of course, it may be a while before the system can be used to treat humans. “The big test is if it can work just as well, or even better in animal trials,” says Dr. Mortimer Poncz of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. If it’s not successful in this context, it’s not a viable solution. He notes, however, that “it is a nice step forward.”
Megakaryocytes cultured from patients could also allow researchers to design patient-specific treatment courses. The researchers hope future applications will go beyond blood disorders, and include healing ulcers and burns, regenerating bone tissue for dentistry and even certain kinds of plastic surgery.
체외에서 혈소판 만든다
혈소판 기능 장애 치료법에는 단점이 많다. 혈소판 수혈이 일반적이지만 기증자가 필요하고, 면역반응으로 인한 합병증이 잦고, 예측 불가능하다. 때로는 항체(면역세포)가 혈소판을 공격하지 않도록 약을 처방하기도 한다. 최후 수단은 환자의 비장을 떼어내는 방법이다. 항체가 생성되는 부위를 상당부분 제거하게 된다. 하지만 그래도 혈소판 수치가 항상 높아지는 건 아니다.
그러나 미국 매사추세츠주 소재 터프츠대 공학대학과 이탈리아 파비아대학 연구팀이 해결책을 찾아냈다고 주장한다. 기능적인 인간 혈소판을 환자의 체외에서 만드는 방법이다. 체내 혈소판 성장을 촉진하는 인체의 골수 환경과 똑같은 기능을 하는 모델을 개발했다.
연구팀은 체외에서 골수의 다공성 환경을 모방할 수 있었다. 실크·콜라겐·피브로넥틴(동물 세포 표면의 당단백질)으로 실처럼 마이크로튜브를 자아내 투과성의 실크 스펀지로 감싸는 방법이다. 그런 환경이 일단 형성되면 연구팀은 환자에게서 배양된 거핵세포(혈소판을 만드는 세포)를 그 시스템 안에 심어 넣었다. 거핵세포들은 실제 골수 안에 있을 때처럼 반응해 혈소판 생성 작업에 착수했다. 혈소판 제조 시스템을 손에 넣은 셈이다.
연구팀 대표 중 한 명인 데이비드 카플란 박사에 따르면 실크가 그 과정의 열쇠를 쥐고 있다. 실크는 다양한 수준의 경도와 갖가지 형태로 변형 가능한 구조를 갖고 있다. 연구팀의 조사 결과, 진짜 혈소판의 형성과 배출에서 그런 기능이 영향을 미쳤다. 무엇보다도 실크는 혈소판의 응고를 유발하지 않는다. 그 시스템에서 기능적인 혈소판을 수확해 나중에 사용할 수 있다는 의미다. 기증자 혈소판으로 인해 생기는 품질과 저장 문제도 해결된다.
그 시스템은 건강한 사람의 골수만큼 혈소판을 많이 만들지는 못한다. 하지만 연구원들은 생산량을 늘릴 수 있다고 낙관한다. 물론 그 시스템을 사람의 치료에 사용하려면 시간이 걸릴지도 모른다. “동물 실험에서도 그만큼 효과가 있을지 또는 더 좋을지가 큰 시험대”라고 필라델피아 아동병원의 모타이머 폰츠 박사가 말했다. 이 같은 환경에서 성공하지 못할 경우 실효성 있는 해법이 아니다. 그래도 “상당한 발전”이라고 그는 평한다.
과학자들이 환자에게서 배양된 거핵세포를 이용해 환자의 맞춤 치료 과정을 설계할 수도 있다. 연구팀은 이 기법이 장차 혈액 질환을 넘어 다양하게 응용되기를 희망한다. 궤양과 화상 치료, 치과용 뼈조직 재생, 나아가 특정한 유의 성형수술 등이다.
- 번역 차진우
ⓒ이코노미스트(https://economist.co.kr) '내일을 위한 경제뉴스 이코노미스트' 무단 전재 및 재배포 금지








![면봉 개수 → 오겜2 참가자 세기.. 최도전, 정직해서 재밌다 [김지혜의 ★튜브]](https://image.isplus.com/data/isp/image/2025/12/21/isp20251221000019.400.0.jpg)
![갓 잡은 갈치를 입속에... 현대판 ‘나는 자연인이다’ 준아 [김지혜의 ★튜브]](https://image.isplus.com/data/isp/image/2025/11/21/isp20251121000010.400.0.jpg)



당신이 좋아할 만한 기사
브랜드 미디어
브랜드 미디어
한상진, 유재석 전화 받고 “엉엉 울었다”... 미담 공개
대한민국 스포츠·연예의 살아있는 역사 일간스포츠일간스포츠
이데일리
일간스포츠
‘갑질 의혹’ 박나래, 전 매니저에 명품 시계 선물 해줬나... 흔적 有 [왓IS]
대한민국 스포츠·연예의 살아있는 역사 일간스포츠일간스포츠
일간스포츠
일간스포츠
달러 들여오면 세제 혜택 준다…환율 1450원대까지 급락(종합)
세상을 올바르게,세상을 따뜻하게이데일리
이데일리
이데일리
국내 사모펀드 ‘관망’, 조 단위 M&A는 글로벌 PEF 독무대
성공 투자의 동반자마켓인
마켓인
마켓인
'플루빅토 독점 구조 흔들까'…효능·부작용 앞세운 셀비온, 5400억 정조준
바이오 성공 투자, 1%를 위한 길라잡이팜이데일리
팜이데일리
팜이데일리